A Curator network
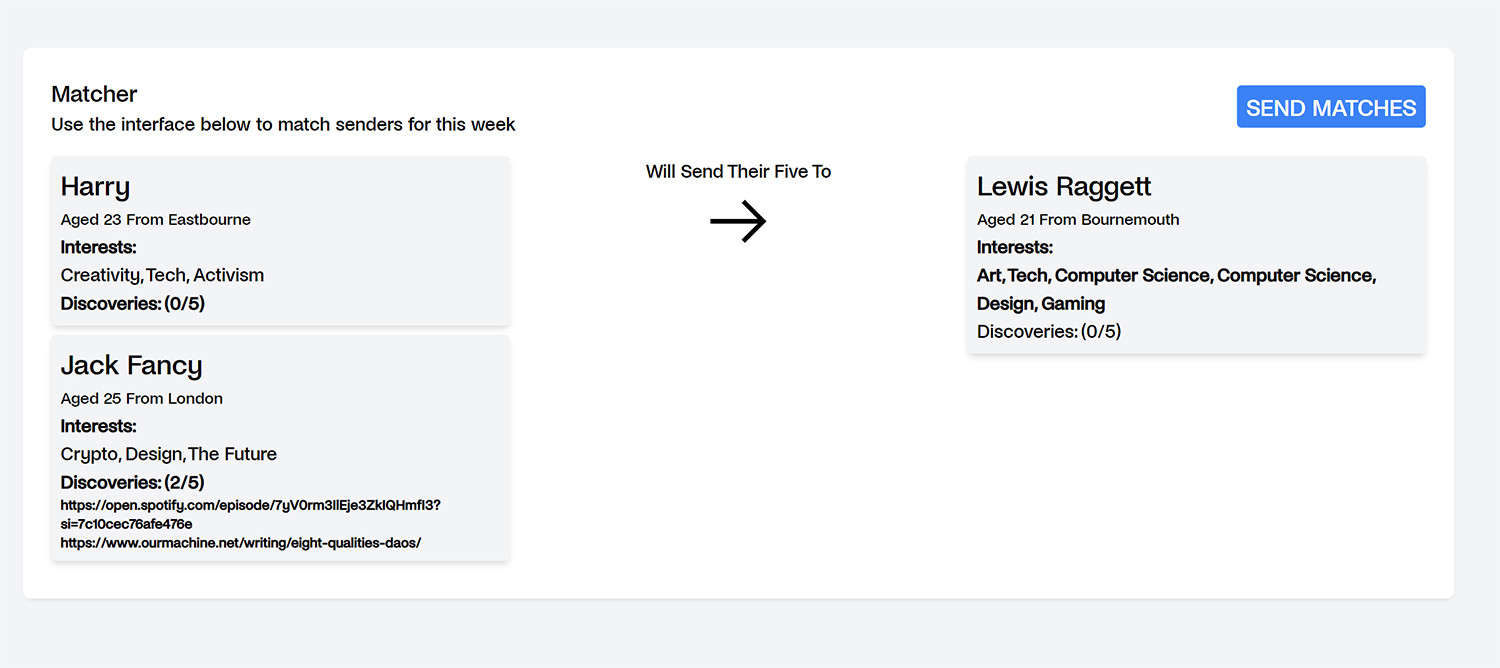
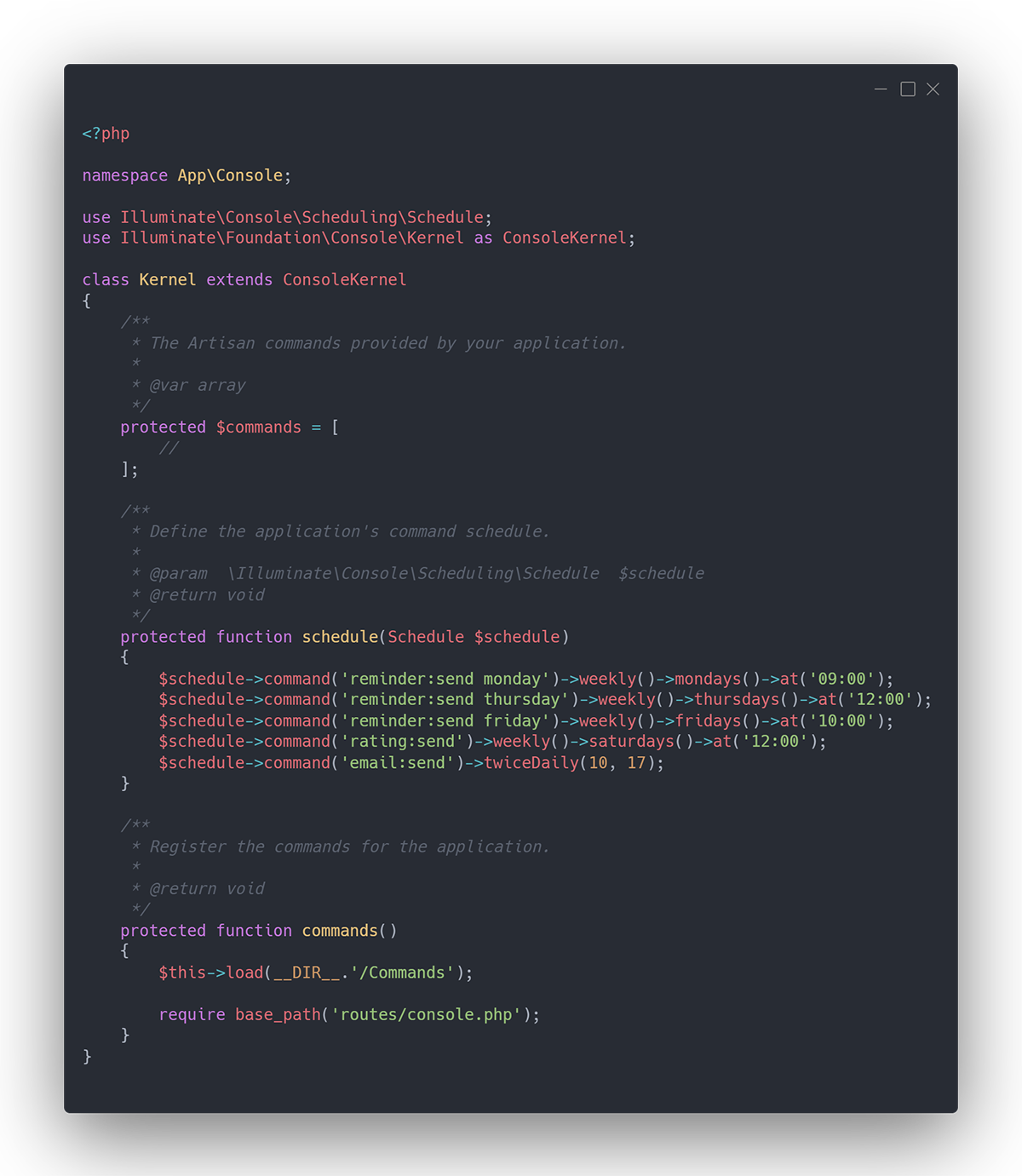
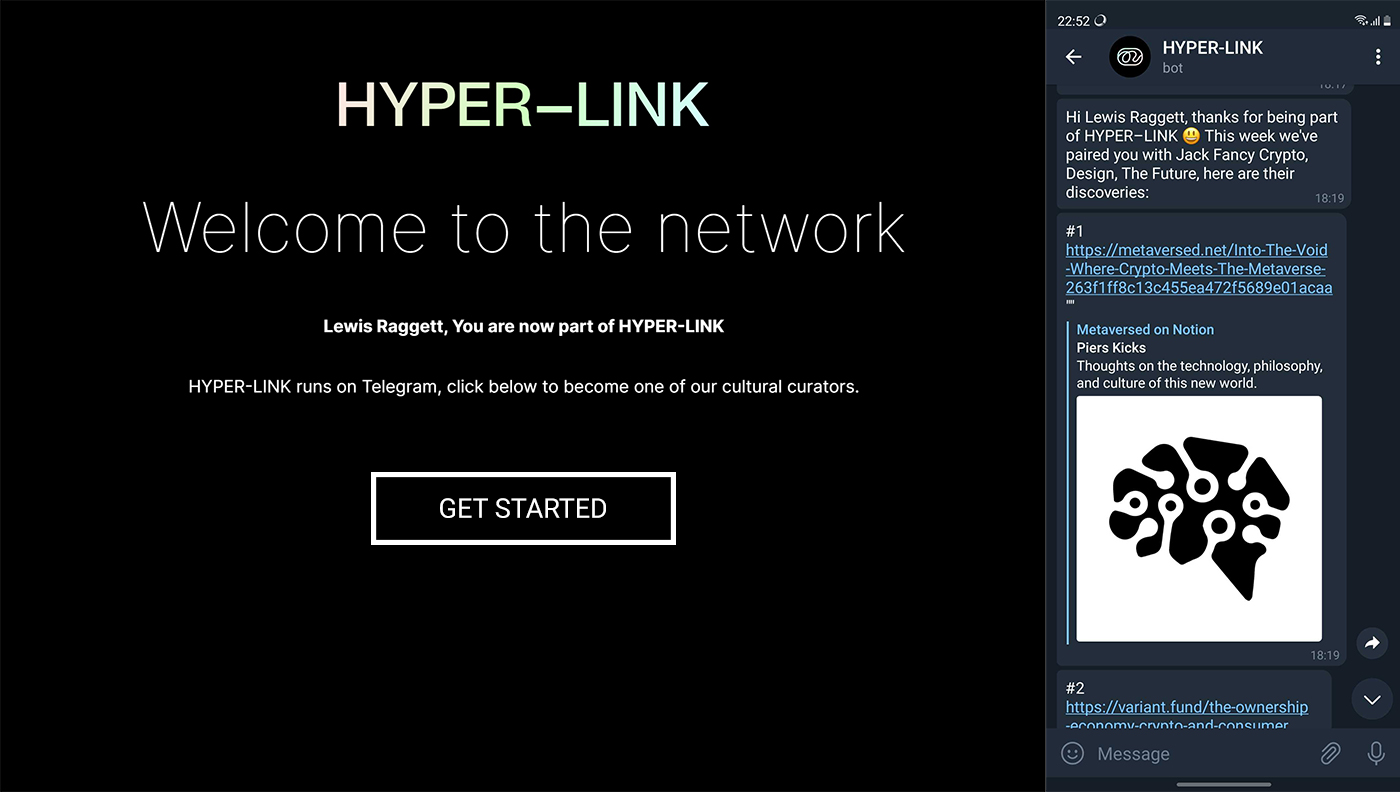
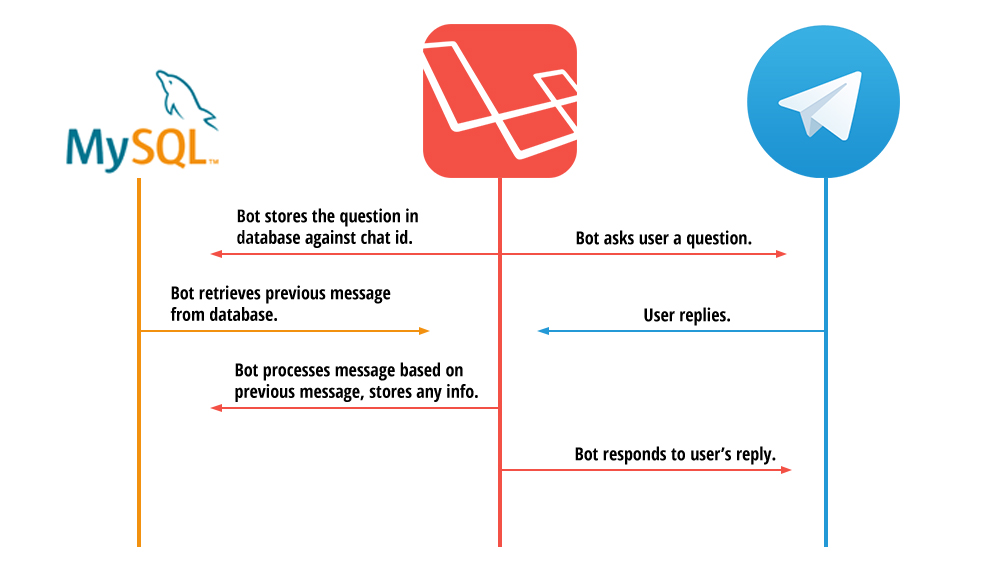
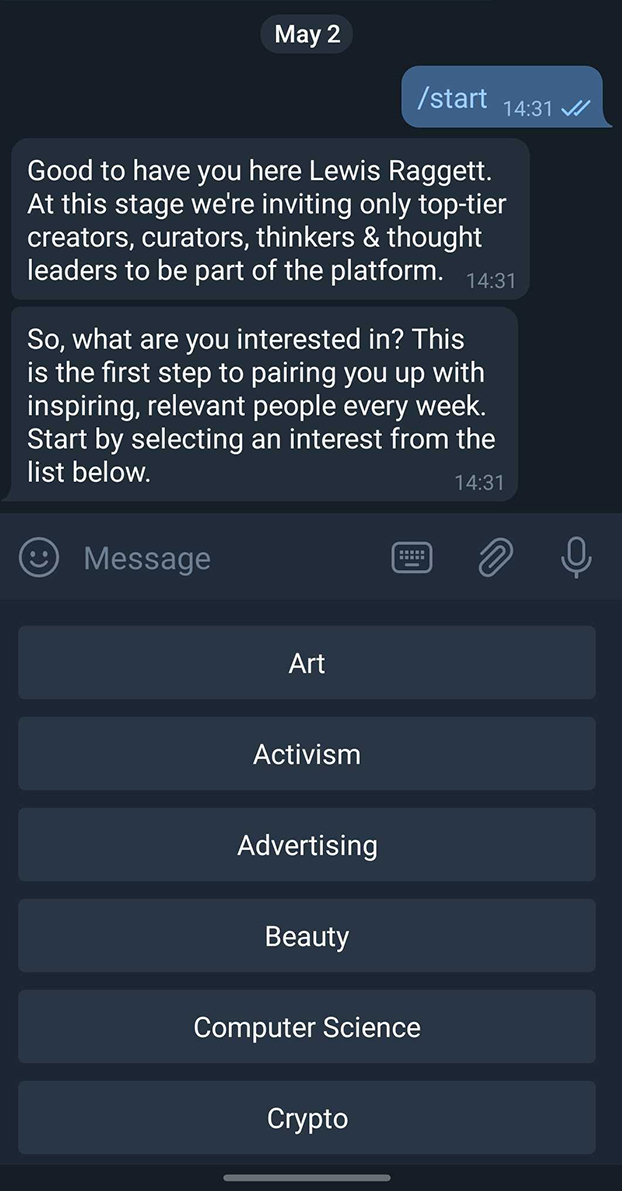
HYPER-LINK is a project set up by Jack Fancy and Harry Eastham with the aim of linking creative individuals to allow them to share their discoveries throughout the week. The premise is that members of the network would send 5 articles, post casts, videos etc. to the pair on WhatsApp a week. Jack and Harry would then send these sets of links to another member based on their interests, the process is very similar to a secret Santa set up. Inevitably, as their network grew, managing so many people was becoming quite difficult to they decided they required a chat bot to automate it. Telegram has become a more popular platform after WhatsApp was bought by Facebook so they would use it as their platform.
They came into contact with me through a family friend who had seen my work and I agreed to build the chatbot as I was curious about the development process and thought it would be a good project to learn from.

.png)
.png)
.png)